146. LRU Cache
내 풀이 vs. 답안 풀이
| 내 풀이 | 답안 풀이 | |
| LRU cache 구현하는 data structure (단, get()과 put()의 시간 복잡도가 $O(1)$이어야 함) |
Dictionary | Dictionary & Double Linked List cf) Key를 가진 Double Linked List는 시간 복잡도가 항상 $O(1)$ |
| Edge case (list is empty and capacity is 1) |
생각지도 못한 케이스라 방어로직 만들지 않음 | head와 tail에 대한 dummy 노드 생성 |
| Least Recently Used (LRU)에 대한 이해 | least랑 latest 헷갈려서 가장 최근에 사용한 key를 삭제해야 한다고 생각함.. ah... | 가장 오래 사용하지 않은 key 삭제 |
| Update 처리 | update도 그 key를 사용한 것이라 생각 못함 | 상식적으로 update도 그 key를 사용한 것 |
내 답안
class LRUCache:
del_key = -1
cache = {}
def __init__(self, capacity: int):
# Initialize the LRU cache with positive size capacity
self.capacity = capacity
def get(self, key: int) -> int:
# Return the value of the key if the key exists
try:
return self.cache[key]
# otherwise return -1
except KeyError:
return -1
def put(self, key: int, value: int) -> None:
## If the number of keys exceeds the capacity from this operation, evict the least recently used key.
if self.del_key != -1:
del self.cache[self.del_key - 1]
elif len(self.cache) + 1 > self.capacity:
self.del_key = max(self.cache)
del self.cache[self.del_key]
# Update the value of the key if the key exists
# Otherwise, add the key-value pair to the cache
self.cache[key] = value
# Your LRUCache object will be instantiated and called as such:
# obj = LRUCache(capacity)
# param_1 = obj.get(key)
# obj.put(key,value) 0
0
답안 예시
class ListNode:
def __init__(self, key, val):
self.key = key
self.val = val
self.next = None
self.prev = None
class LRUCache:
def __init__(self, capacity: int):
self.capacity = capacity
self.dic = {}
self.head = ListNode(-1, -1)
self.tail = ListNode(-1, -1)
self.head.next = self.tail
self.tail.prev = self.head
def get(self, key: int) -> int:
if key not in self.dic:
return -1
node = self.dic[key]
self.remove(node)
self.add(node)
return node.val
def put(self, key: int, value: int) -> None:
if key in self.dic:
old_node = self.dic[key]
self.remove(old_node)
node = ListNode(key, value)
self.dic[key] = node
self.add(node)
if len(self.dic) > self.capacity:
node_to_delete = self.head.next
self.remove(node_to_delete)
del self.dic[node_to_delete.key]
def add(self, node):
previous_end = self.tail.prev
previous_end.next = node
node.prev = previous_end
node.next = self.tail
self.tail.prev = node
def remove(self, node):
node.prev.next = node.next
node.next.prev = node.prev
# Your LRUCache object will be instantiated and called as such:
# obj = LRUCache(capacity)
# param_1 = obj.get(key)
# obj.put(key,value)

solution 보는데 필요한 기능들을 정의하고 이 모든 기능에 맞는 data structure가 어떤 것인지 고민하는 이 문제 풀이 접근 방식이 너무 좋은 것 같다. 앞으로 알고리즘 문제 풀 때 이렇게 접근해야겠다! 이렇게 했으면 4~6이 딕셔너리로 안된다는 것을 알고 다른 data structure를 고민했을 거고, 그러면 문제를 좀 더 빨리 쉽게 풀 수 있었을 것이다.
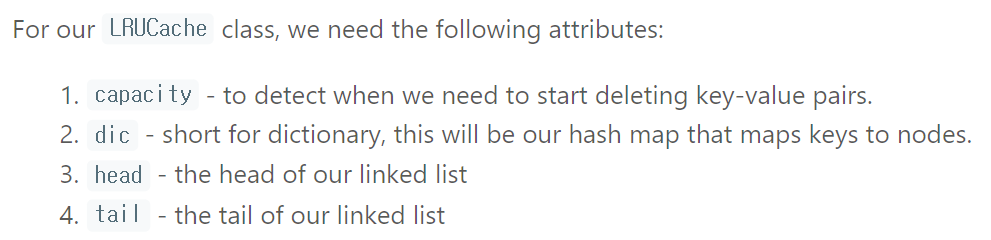
마찬가지로 필요한 기능에 맞는 data structure를 정한 후에는 필요한 특징들을 정리해 봐야겠다.
개념 정리
- 해시맵(Hash Map), 해시 테이블(Hash Table) (>>출처)
- Key-value pairs를 저장하는 data structure가 필요하면 딕셔너리 떠올리기!
(Python의 해시맵으로 구성된 자료구조는 딕셔너리이기 때문) - 특징
- 순차적으로 데이터를 저장하지 않습니다.
- Key를 통해서 Value값을 얻습니다.
- Value값은 중복가능 하지만 Key는 중복될 수 없습니다.
- 수정 가능합니다.(mutable)
- Key-value pairs를 저장하는 data structure가 필요하면 딕셔너리 떠올리기!
- 큐 (Queue)
- 가장 큰 특징 : FIFO -> 이런 규칙이 있다면 큐를 떠올리기!
출처 : https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Queue_%28abstract_data_type%29
- 가장 큰 특징 : FIFO -> 이런 규칙이 있다면 큐를 떠올리기!
- 단방향 연결 리스트 (Simply Linked List)
- 다른 노드를 지시하는 포인터가 앞에서 뒤의 단방향으로 설정
- 동적으로 할당된 메모리의 연결 구조로 표현
- 노드 구조 : data, next
- 단점
- 반대 방향으로 움직이는 연산에 대해 많은 시간을 소비
- Sequential Access
ex) 비상연락망에서 23번째 학생한테 연속하려면 22번 연락해야 함
- Array vs. Linked List
- 더 많은 차이점은 https://byjus.com/gate/difference-between-array-and-linked-list/ 참고
- cf) List != Array in Python (>>출처)
- List는 다양한 data type을 담을 수 있으나
- Array는 한 가지의 data type만 담을 수 있음
| 접근성 | 메모리 사용의 효율성 | 추가/삭제 | |
| Array | O Direct access라 접근 속도가 굉장히 빠르다(동일한 type의 데이터가 연속적으로 할당되어 있으므로 몇 번째 데이터가 어디 있는지 한 번에 찾을 수 있다.) |
X maximum을 한꺼번에 할당받아야 해서 다 안 쓰면 메모리를 낭비할 수 있음. |
X (어려움) maximum을 설정해야 하고 그 이상의 데이터는 처리하지 못하므로 추가, 삭제가 어려움. 따라서, 추가/삭제할 필요 없이 빨리 꺼내오는 게 목적이면 array 사용 |
| Linked List | X | O | O (쉬움) 메모리를 비연속적으로 할당하기 때문에 maximun 설정할 필요가 X |
- 양방향 연결 리스트 (Doubly Linked List)
- 다른 노드를 지시하는 포인터가 양방향으로 설정
- 노드 구조 : prior, data, next
- Simply Linked List vs. Doubly Linked List
- Simply Linked List
- 마지막 노드에서 next하면 null
- 추가(insert)/삭제(delete) 시간 복잡도가 $O(N)$ (head or tail에서)
- Doubly Linked List
- 마지막 노드에서 next하면 처음으로 돌아감
- 추가(insert)/삭제(delete) 시간 복잡도가 $O(1)$ (head or tail에서, 중간 노드라면 $O(N)$)
- 더 많은 차이점은 https://byjus.com/gate/difference-between-singly-linked-list-doubly-linked-list/ 참고
- Simply Linked List
- Python에서 null은 None (>>출처)
- edge case : 큰 영향을 끼치는 예상하지 못한 bug나 issue (>>출처)
'Computer Science > 알고리즘' 카테고리의 다른 글
| [LeetCode/Easy] 20. Valid Parentheses (1) | 2024.01.21 |
|---|---|
| [LeetCode/Easy] 1. Two Sum (0) | 2024.01.18 |
| [이코테] 게임 개발 (0) | 2022.01.14 |
| [이코테] 왕실의 나이트 (0) | 2022.01.13 |
| [이코테] 시각 (0) | 2022.01.06 |




